Common Urologic Problems and How You Can Treat Them
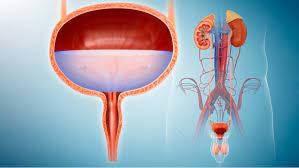
The urinary system works hard to regulate, manage, and eliminate urinary waste products. It contains many moving parts such as the kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra. Like any other organ or system in the body, there can be problems with the urinary system. These problems or conditions are commonly referred to as urological problems or urological diseases. Urological problems can occur regardless of age, gender, or ethnicity. In both men and women, this directly affects the urinary tract and how urine is excreted. In men, urological problems can also affect the reproductive organs.
The mission of Allied Pharmacy is to improve patient health through a rigorous commitment to excellence. This is accomplished by educating and engaging patients. By working with doctors, health plans, and manufacturers, we also help patients address their individual medication needs and challenges.
Urinary incontinence
In the United States, he said, more than 15 million people suffer from urinary incontinence. There are many different causes of urinary incontinence, some of which are listed below. Diabetes, childbirth, bladder or sphincter weakness, spinal cord injury, certain medical conditions, and even severe constipation. Simple lifestyle changes can often help manage urinary incontinence. If you still struggle with incontinence, talk to your doctor about corrective surgery.
Stress Incontinence
Similarly, stress incontinence can lead to leakage. Both men and women suffer from stress incontinence, but it occurs more commonly in women. Stress incontinence happens when the muscles that support your bladder and help regulate the release of urine are weakened the valve-like muscles in your urethra struggle to stay closed. Aside from lifestyle changes, stress incontinence can be treated through urethral bulking (in women) or implanting an artificial urinary sphincter to help stimulate a competent bladder outlet.
Overactive Bladder
Overactive bladder (OAB) occurs when the bladder can’t store urine properly and leads to an involuntary loss of urine due to an intense and sudden urge to urinate. The muscles of your bladder may start to contract involuntary, almost like spasms. There are a few causes of overactive bladder, including neurological disorders, diabetes, UTIs, bladder stones, tumors, or simply getting older. The best ways to prevent overactive bladder include staying active, maintaining a healthy weight, and taking a proactive approach to managing chronic conditions like diabetes. To treat overactive bladder, your doctor will work with you to establish a schedule of bathroom times to better train your bladder. There is also medication available to further control overactive bladder.
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Urinary tract infections are the most common type of urologic problem and occur much more frequently in women. In fact, nearly 60% of women will experience a UTI at some point in their lives, but UTIs affect only 12% of men. The main symptoms when having a UTI are a burning sensation or frequent urination. To properly diagnose a UTI, a doctor should do a urine culture. Fortunately, urinary tract infections can be easily treated with antibiotics. It is important to treat them as soon as possible to prevent further infections and eliminate complications. If your UTI recurs, see your doctor now.
Kidney and ureteral stones
Kidney and ureteral stones occur when crystal-like particles develop in the urine and small particles grow around the crystals. Most stones pass spontaneously, but large stones often require surgery or special treatment. One of the most commonly used techniques is extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL), which uses sound waves to break stones into smaller pieces.
Urological Issues Specific to Women
Women naturally have a short urethra, which increases urological problems. In addition to the increase in urinary tract infections, women are prone to some specific urological problems.
Pelvic floor dysfunction
The pelvic floor acts as a support system for the bladder, vagina and rectum. During life, especially after childbirth, these muscles can become inflamed and inflamed. Urination may be difficult because the pelvic floor needs to be relaxed for urination or pelvic floor dysfunction causes pain. The best treatment is to learn how to relax your pelvic floor muscles with the help of a professional therapist. This reduces stress, makes it easier to urinate, and reduces pain. If not, your doctor will suggest vaginal or intramuscular injections.
Pelvic organ prolapsed
Although this is less common, pelvic organ prolapsed occurs. It occurs when organs shift and fall out of their normal position due to areas of weakness in the walls and muscles of the vagina It is most commonly caused by trauma during childbirth, and women often experience a sensation or swelling in the vagina near the vagina when sitting. If you experience excessive discomfort, surgically inserting a silicone or rubber diaphragm can alleviate the problem.
Incontinence after pregnancy
Pregnancy puts a lot of strain on the urinary tract. After giving birth, laughing, coughing, sneezing, or doing any physical activity can cause accidental leakage. Fortunately, post-pregnancy urinary incontinence can be treated. You can make an appointment for a test, which is the first step, after which your doctor will present you with several treatment options. During urinary incontinence, Kegel gel is recommended to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles.